Foreword(写在前面)
今天给大家分享的这篇文章hifiasm是2021年2月份哈佛的Heng Li发在Nature methods上的一篇关于基因组拼接的新作,Heng Li是生物信息算法这方面的大佬了,BEA-MEM,minimap2,wtdbg2等等,做了很多序列比对、拼接方面的优秀算法。今天这篇讲的是关于单倍型分辨率的从头拼接算法。先做一个简单的介绍,所谓的Haplotype-resolved和phased assembly是一个意思(见Heng Li去年的一篇nature biotech的摘要Chromosome-scale, haplotype-resolved assembly of human genomes),指的就是我们能够重构出多倍体物种的所有的单倍型。就人类的基因组而言,对于每对同源染色体其实我们有父源和母源两条,上面可能携带了不同的等位基因,但是传统的assembly方法都忽略了两条染色体的差异,其实最后生成的contigs是类似consensus的sequence。其中的原因也比较显然,因为我们测序的时候将所有基因组随即打碎,我们也分辨不出父源母源的序列。如下图,一般我们称左边得到的concensus序列叫做Genotype,而我们的目标是phase出来父源母源两条序列。那么将一对等位基因都分别还原出来,对于遗传学研究、各种疾病检测的意义肯定是不言而喻的。
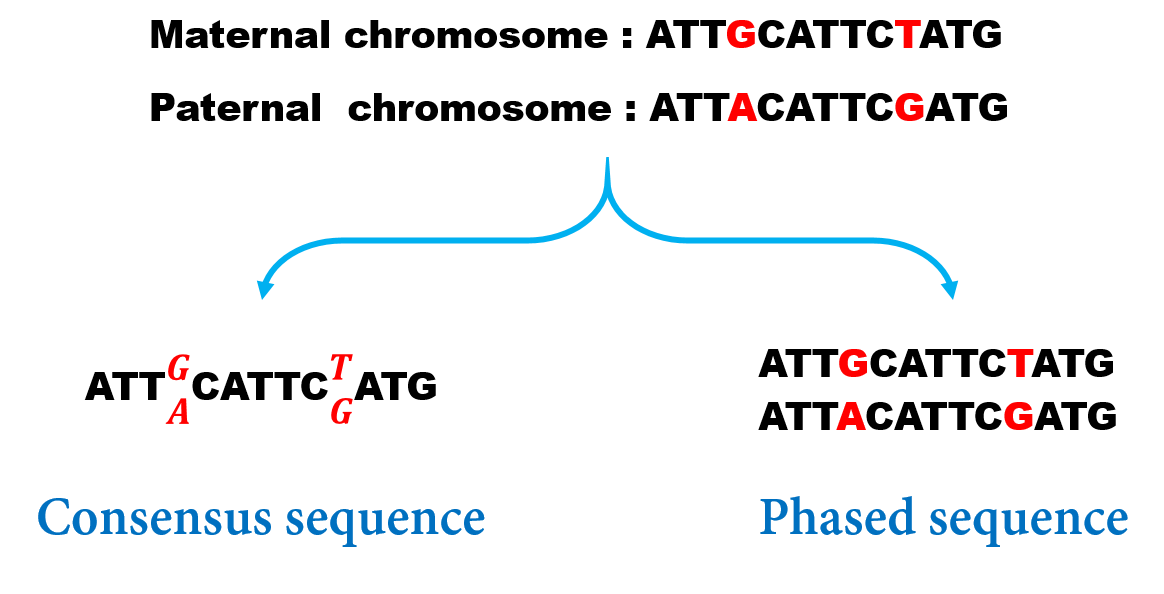
Fig.1 传统拼接的consensus序列 Vs phased序列.
那么,我们有什么手段可以进行phasing呢?
1.首先,最直接的方法,我们可以再测该个体的母亲和父亲的基因组,当然这个方法缺点就在于我们又多测了两个基因组,而且有时候我们可能都得不到父母的基因组;其次,如果父母都是杂合子AB,那么我们也不能判断出来子代等位基因AB的来源;在2018年,National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA)的两个科学家在nature biotech上发布了Trio binning算法(Trio指的就是Father-mather-child三样本),我们可以看一些Heng Li在20年7月发的一篇natrue biotech对trio binning的评价
FALCON-Phase, which extends FALCON-Unzip …… but it cannot achieve chromosome-long phasing. Trio binning is the only published method that can do this, plus the assembly and phasing of entire chromosomes. …… However, trio binning is unable to resolve regions heterozygous in all three samples in the trio and will leave such regions unphased. More importantly, parental samples are not always available—for example, for samples caught in the wild or when parents are deceased. For Mendelian diseases, de novo mutations in the offspring will not be captured and phased with the parents if there are no other heterozygotes nearby. This limits the application of trio binning.
害,这篇FALCON-Phase在19年4月就挂在biorxiv上了,21年4月28号也就是前几天才终于发在了Nature Communications
下面是trio binning的一个workflow,红色表示母源的染色体,蓝色表示父源,然后对于父母的基因组short-read测序,然后我们可以得到k-mers的一个分布情况,也就是b中的韦恩图。根据这个分布,对于子代基因组的long-read进行分类,分为父源、母源以及unassigned,然后分别进行组装。
Fig.2 Outline of trio binning and haplotype assembly1.
2.第二种是LD phase,也就是根据连锁不平衡,有些区域的染色体在减数分裂同源染色体重组的时候,更不容易重组,经常连锁在一起,我们也可以构建一些遗传的统计模型,HMM模型来预测我们所测样本的可能单倍型,这个涉及遗传的知识比较多,就不再详述,当然了问题也很多,LD方法对于罕见突变或者个体特有的突变完全无能为力;
3.Physical phase,也就是我们不依赖任何外部的信息,就从该个体的基因组测序结果进行重构,因为从本质上,每一个read一定来自同一个单倍型,所以其实就是一个局部的phase,然后我们的目标是将这些局部的phase延伸成尽可能长的单倍型序列,所以我们最终目标是,将整个姐妹染色单体分别重构,或者说我们想得到telomere-to-telomere的phase。这也是我们这篇文章所做的phasing算法就属于这类方法。
Background
然后我们先来看几个概念,这几个概念的名词解释来自于前几天Heng Li自己发的Blog Heng Li的博客
Haplotig: a contig that comes from the same haplotype. In an unphased assembly, a contig may join alleles from different parental haplotypes in a diploid or polyploid genome.
Primary assembly: a (haploid) complete assembly with long stretches of phased blocks.
Haplotype-resolved assembly: sets of (haploid) complete assemblies consisting of haplotigs, representing an entire diploid/polyploid genome. This concept has been inconsistently used in publications without a clear definition. The above is my take in our recent papers.
也就是Haplotig表示序列来自同一单倍型的contig,而Haplotype-resolved assembly表示一些(haploid) complete assemblies的集合,也就是这些组装(由haplotigs构成)共同代表了整个二(多)倍体基因组。所谓的Primary assembly就是一个中间阶段吧,由一些已经phased的较长序列组成,但是其实Primary assembly的结构是mosaic的,后文将会再次提到,并详细介绍。
这篇文章使用的是HiFi-read来进行组装的,如果不熟悉三代测序中Pacbio方法中的CCS序列(HiFi-read),可以看下面这个图,根据我的调研,之前官网文档上表示CCS序列长度在500bp-3kb,较新的数据根据下面这个篇文章所述,read平均长度可以达到13.5(kb),准确度在99.8%。之所以准确度比正常的三代测序要高,是因为其对一个read循环测了多次,因为错误是随机的,所以可以相互矫正.关于CCS(HiFi-read)的详细内容,可以参见这篇19年的nature biotech,是Pacbio公司发表的Accurate circular consensus long-read sequencing improves variant detection and assembly of a human genome.
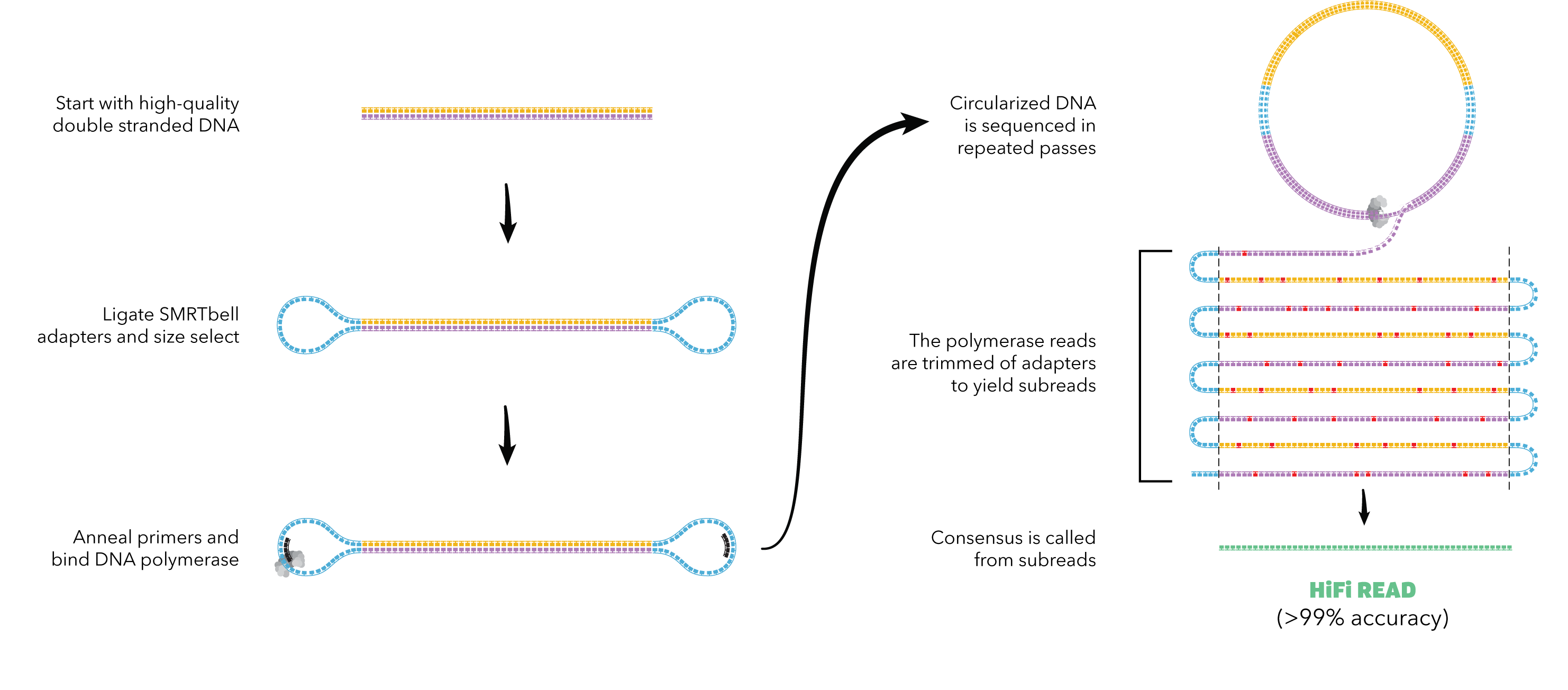
Fig.3 How to get HiFi-read2.
A great challenge to the assembly of heterozygous samples is caused by the 5–15% sequencing error rate of older long reads. With this high error rate, it is difficult to distinguish errors from heterozygotes occurring at a rate of <0.1% in humans. The recent availability of high-fidelity (HiFi) reads produced by PacBio has changed the equation.Generated from the consensus of multiple sequences of the same DNA molecule, HiFi reads have a much lower error rate of <1%. With HiFi, standard trio binning can produce contigs of 17 Mb.
为什么使用HiFi-read,其实也很好理解,因为同源染色体本身的差距就很小,根据这篇文章所讲,人类的杂合子的差距在0.1%以内,如果read本身误差很大,那么对于回复更精确的同源序列就更是天方夜谭了。 PS:个人认为,可能正是HiFi-read准确度、长度都大大提高,所以才使得单倍型的组装进一步发展,使得染色体规模的单倍型组装成为可能(确实最近这方面的文章在nature子刊上发表了很多).
Introduction
仅用read进行phasing
Most of them (assemblers) collapse different homologous haplotypes into a consensus representation with heterozygous alleles frequently switching in the consensus. …… Falcon-Unzip recovers heterozygous alleles by ‘unzipping’ them in an initial collapsed assembly. It produces a pair of assemblies, one primary assembly representing a mosaic of homologous haplotypes, and one alternate assembly composed of short haplotype-specific contigs (haplotigs) for alleles absent from the primary assembly. The alternate assembly is often fragmented and does not represent a complete haplotype, making it less useful in practice.
目前已知的很多三代基因组拼接软件得到是序列都是同源染色体的consensus序列。 Falcon-Unzip选择了从collapsed assembly中“unzip”出等位基因,然后得到两组assembly,一个称为primary assembly,其中的contig是同源的单倍型的序列交错出现的,也就是所谓mosaic的结构,另外一套assembly是一些较短的Haplotig,也就是primary contig中一些基因的相应的等位基因序列如下图所示,所以其实Flacon-Unzip并没有实现整个染色体规模的phased,两个assembly都不代表任何一个单倍型。Falcon-phase是前几天4月28号发在NC上的,在biorxiv上挂了两年,也只是借用了Hi-C数据使得haplotig更长,仍没达到染色体规模。
Fig.4 Falcon output3.
Trio binning addresses these issues by globally partitioning long reads upfront with parental short reads and then performing two separate assemblies on the partitioned reads. This strategy works well for samples with high heterozygosity, but for a human sample sequenced with noisy long reads, it only produces fragmented assemblies with ~1.2-Mb contigs.
刚才我们简单介绍了Trio binning的原理,因为其根据k-mers的父源、母源来对子代long-reads进行分类,其实文章用了Angus and Brahman两个品种 的牛(安格斯和婆罗门)做了实杂交实验,再进行测序,但是对于亲缘关系更近的人类,trio binning的contigs长度就大大减小了,因为噪声更多,分辨read属于父母哪一方更困难。因此,组装出来的contigs的连续性就会变差。
使用额外技术phasing
Recent works relying on high-throughput chromosomal confirmation capture (Hi-C) or strand sequencing (Strand-seq) read binning can achieve better contiguity and phasing accuracy. These pre-binning algorithms all use short k-mers or short reads to partition HiFi reads. They may not identify haplotype-specific markers in complex regions and result in wrong read partitions, which will negatively affect the assembly, as shown later. In addition, both Hi-C and Strand-seq binning start with a collapsed assembly and have the same issues as Falcon-Unzip.
刚才提到的20年7月Heng Li发表在Nature Biotech的Chromosome-scale, haplotype-resolved assembly of human genomes,就利用了Hi-C染色体结构数据来延长phased的片段;另一种技术称为Strand-seq,大致的原理图如下,首先在细胞复制的时候加入一种叫做BrdU的碱基类似物,这种物质可以在UV射线照射下降解,所以细胞复制新合成的链后面就会被降解,被保留的就是原始细胞的模板链。那么在该细胞细胞分类得到的子代细胞中,就有下面三种类型,WW、CC、WC(我们把模板链的正链记为Watson(W)链,反链记为Crick(C)链).那么对于WC这种类型的子代细胞,我们进行测序,将read回贴到参考基因组上,很容易就可以分辨出来read属于父源的染色体还是母源的染色体(因为比对在参考基因组W、C链来分别来自两条姐妹染色体) 对于利用Strand-seq来phased基因组的,可以看这两篇文章
Direct chromosome-length haplotyping by single-cell sequencing
Fig.5 Strand-seq4.
但是上述方法,思路都是先将HiFi reads进行分类(依赖k-mers或者short reads),这会导致read分类的错误。错误原因与上面所述的类似,亲本可能在某个位点都是杂合子,或者父本是杂合的,母亲是纯合子,我们根据k-mers仍然分不出来子代的read属于哪一方。
unitig graph
就是在构图(string graph),并进行transitive reduction(后面方法部分介绍了这个步骤)之后,将没有歧义的path视为一个unitig。
Methods
Overview of hifiasm
Hifiasm有两种模式,如果是只有子代的HiFi-read,就只能得到左侧primary assembly;如果有亲代的short read测序,就可以得到右侧单倍型分辨率的assembly。大致的过程就是先矫正(但是保护了同源染色体差异的矫正),再构图,然后用不同方法解开bubble。
Fig.6 Overview of hifiasm.
Haplotype-aware error correction
Hifiasm performs all-versus-all read overlap alignment and then corrects sequencing errors.Given a target read to be corrected, hifiasm inspects the alignment of reads overlapping with the target read.
Def: A position on the target read is said to be informative if there are two types of A/C/G/T bases (gaps ignored) at the position in the alignment, and each type is supported by at least three reads.
Def: A read overlapping with the target read is inconsistent with the target if there are informative positions in the overlap and the read is not identical to the target read across all these positions; accordingly, the overlap between this and the target read is inconsistent.
Inconsistent reads theoretically originate from a haplotype different from the target read. Hifiasm only uses consistent reads to correct the target read.
首先我们执行all-versus-all overlap alignment,然后进行矫正,对于待矫正的read称为Target read(简记为T),检查与T有overlap的所有reads的alignment情况,我们给出下面两个定义
Def_1: T中的某个位置称为informative,如果
(1)该位置的比对中存在两种碱基类型(不包括gap)
(2)每种碱基类型有至少三条read支持
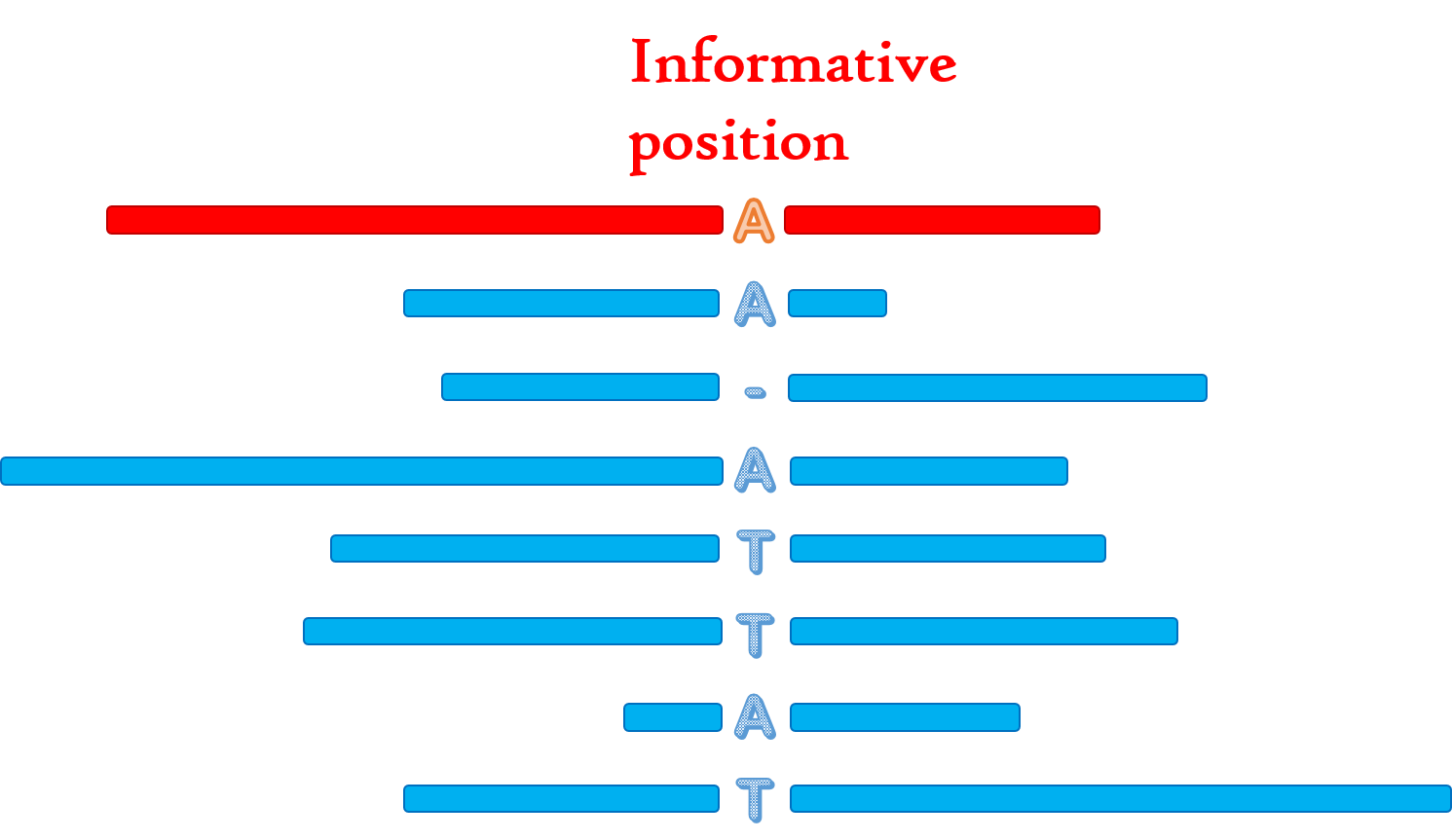 Fig.7 Informative position.
Fig.7 Informative position.
Def_2;我们称一条read R(与T有overlap)相较于T是inconsistent,如果
(1)R与T的overlap中存在informative position
(2)二者informative position上的位置并不完全一致
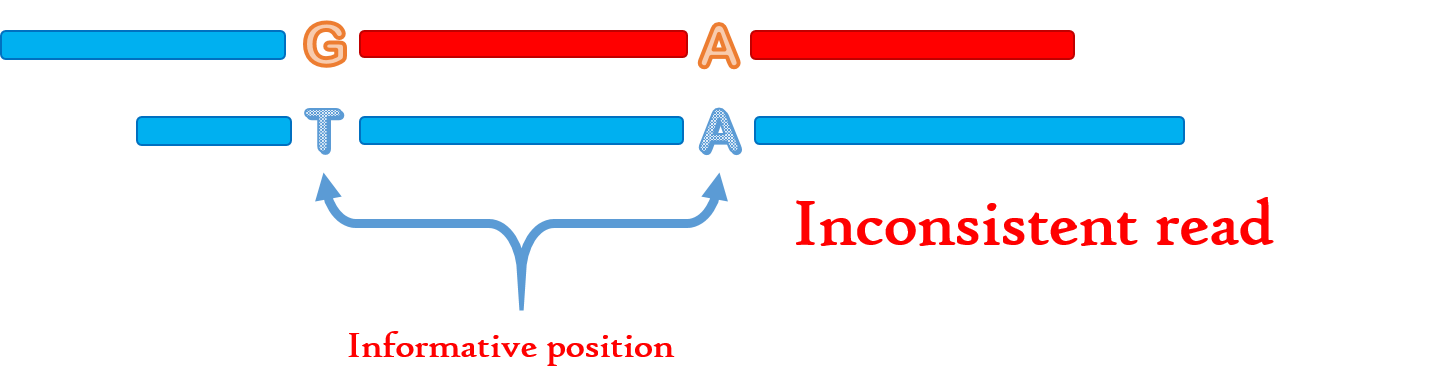 Fig.8 Inconsistent read.
Fig.8 Inconsistent read.
所以对于target read我们只使用consistent read来矫正,矫正的处理方法与Falcon类似,Hifiasm默认执行三轮矫正。
构建phased assembly graphs
The next step is to build the assembly string graph. In this graph, nodes represent oriented reads, and each edge between two nodes represents the overlap between the corresponding two reads. Note that only consistent overlaps are used to build the graph. Because hifiasm builds the graph on top of nearly error-free reads and highly accurate haplotype phasing, the produced assembly graph of hifiasm is simpler and cleaner than those of current assemblers for haploid genomes. However, for diploid genomes or polyploid genomes, its graph becomes more complicated as reads from different haplotypes are clearly separated out by phasing.
下面进行构图,hifiasm采用的是string graph,即顶点表示reads,边表示顶点(reads)之间的overlap序列。注意,图中的边采用的都是consistent overlap。因为我们的目的是还原两个单倍型,所以我们认为consistent overlap连接的两个reads来自于同一条染色体。之所以能这样将read分开,主要是因为HiFi-read的高准确度,保证了我们可以进行这么精准的操作。当然了,因为同源染色体不一致的序列存在,所以图中会出现“bubble”的结构,如下图所示。注意到,如果我们真的从图中给的reads alignment的情况来构图,比下面的图肯定复杂很多,会增加很多边。所以其实,这里面进行了transitive reduction的操作,即如果图中存在$v_{1} \rightarrow v_{2}$,$v_{2} \rightarrow v_{3}$,且$v_{1} \rightarrow v_{3}$这样的情况,那么我们就删除边$v_{1} \rightarrow v_{3}$,一直进行下去,移除类似的边,直到图中不存在为止。这样才真正得到了下面的图。
Fig.9 Bubble5.
构建primary assembly
The construction of the primary assembly aims to produce contigs including one set of haplotypes but may switch subregions between haplotypes. In other words, each subregion in the primary assembly only comes from one haplotype, while the corresponding subregions of other haplotypes are removed as duplications.
什么叫做primary assembly呢,这一步的想达到什么结果呢。前面已经已经粗略的了解primary assembly了,具体来讲,我们先尽可能的保证一组assembly的连续性,这个assembly的每个contig的每个子区域都可以确定完全来自于一种单倍型,然而contig的序列整体来看是在两个单倍型之间反复转换的(如图Fig.9)。同时,我们又保证,每个contig的子区域对应的染色体的区域,其相应的另一条同源染色体的该区域不会存在于primary assembly中。如下图Fig.10所示,上面生成的contig就被选入primary assembly集合中,而下面的序列作为同源区段,暂时被抛弃。
Fig.10 Primary contig6.
Fig.11 Primary assembly5.
理想状态,我们觉得hifiasm得到的phased graph应该是一个长链,然后中间依次有一些“Bubbles”,但是实际上图中还存在一些tips,就是一些单端的分支,类似下面这样,当然也可能不是只有一个点,可能很长。这些位置本来应该是一个bubble,但是因为某些原因破碎了。形成的原因,可能是这个区域的没有被测序read覆盖,也可能是别的原因形成的。
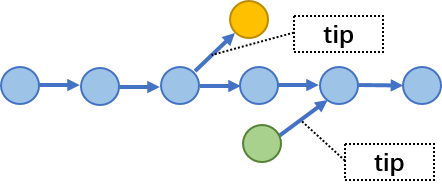
Fig.12 Tips.
First, each bubble in the graph is reduced into a single path using bubble popping. This step removes most duplicated subregions on different haplotypes without hampering the contiguity of primary assembly. Second, given a tip unitig T that is broken in one end but connected to a unitig C in another end, hifiasm checks if there are other unitigs, which are also connected to C, coming from the different haplotypes of T. If such unitigs are identified, hifiasm removes tip T so that unitig C will become longer.
关于第一步bubble poping的按照论文的标准是参考了之前的miniasm Minimap and miniasm: fast mapping and de novo assembly for noisy long sequences,我找了找应该是里面的算法6是关于bubble检测的,我没有仔细看,大致读了一下伪代码,其实思想很简单,就是无向图找最短路的方法,就是path不能超过50kb而已,直到搜索到一个点,其只有一个出边(大致这个思想,具体参见伪代码)。然后,我们从终点开始不断沿着最优的父节点回溯,这样我们就得到了single path。
第二步,如果有一个tips $T$,一段是断裂的,一段连接某个unitig $C$,而$C$又连接另外的unitig $T’$,如果$T’$来自于与$T$相异的染色体(换句话讲,这两个unitig是不是包含之前储存的inconsistent overlap)那么我们删去$T$;如果没有一致性(因为consistent overlap已经构成了边,如果又不是inconsistent overlap,那么这两个unitigs就是比对不上),那么我们将$T$修建,并放入primary assembly中,因为$T$和$T’$不属于同源染色体的相对应位置。
Fig.13 Fix tips6.
Purging heterozygous duplications
To address this duplication challenge, hifiasm reassembles the contigs by building a string graph regarding contigs as nodes, called a purge graph. Given contig A and contig B, we define A as inconsistently overlapping B if there are enough reads of A that are inconsistently overlapped with the reads of B.······In the purge graph of hifiasm, each node is a contig, while an edge between two nodes is an inconsistent overlap between their corresponding contigs. Once the graph is built, hifiasm generates the nonredundant primary assembly by simple graph cleaning.
但是上面的操作还不够精确,对于染色体上高度重复的区域,不能完全保证primary上没有冗余(也就是每个子区域只对应一种单倍型)。所以有下面的处理 Hifiasm对于contigs重新进行assembly,得到string graph(称为purge graph),也就是这是的节点是contigs。
Def:给定contig $A,B$,我们称$A$和$B$是inconsistently overlapping,如果$A$与$B$之间有足够的read是inconsistently overlapped的。
purge graph中的边都是上述inconsistently overlapping的contig构成的,然后我们再执行graph cleaning,也就是去除bubble和tips的程序,我们的得到的最终的nonredundant primary assembly。因为HiFi-read很准,然后phased graph又基本保留了原本的read信息,所以这样操作后这条simple path中的contigs基本上是没有冗余的。
构建haplotype-resolved assembly
hifiasm提供了两种assembly模式,如果没有额外的信息,因为HiFi-read终究还是无法达到染色体的长度级别,上面的primary assembly不可能进一步phase了。
Given parental short reads, hifiasm labels child HiFi reads with the existing k-mer-based algorithm.
When generating a fully phased assemblyfor one haplotype, hifiasm drops reads of different haplotypes from the graph, while using the local phasing information in the graph to correct the mispartition of global phasing. Hifiasm does not drop reads at a single path connecting two bubbles, since these are homozygous reads that must be contained in both haplotypes. For a bubble in which all reads are heterozygous, hifiasm applies bubble popping to select a single best path consisting of the most reads with the expected haplotype label.······hifiasm drops a contig if the haplotype labels of most reads in it are nonexpected.
类似trio binning,hifiasm也预先对于read进行分类,分成了三类,两种单倍型$B$和$Y$,和公有的$G$但是并不完全依赖这个信息,因为我们已经构出来了phased graph,它能够帮助我们修正k-mers分类带来的错误。 当去构建某一个单倍型(假设是$B$)的时候,首先,对于连接两个bubble的single path中的节点(reads),不论其分配到了什么类型,Hifiasm都不舍弃,而是归属于我们想构建的这个单倍型类型$B$中,对于bubble部分,我们选择包含$B$类型的read占比最大的path。所以,即使中间有些read被错误分类,这时候也能被矫正。然后,在如此重新标签以后,我们将$Y$标签的read扔点,剩下的read进行构图。最后,如果我们最终得到的contig中数量最多的单倍型标签不是我们预期的$B$,那么我们也舍弃掉。如下图所示,左侧是先前的binning方法得到的结果,右侧是本文所谓的Graph-binning策略、
Fig.14 Graph-binning5.
Results
Assembling homozygous/heterozygous nonhuman genomes
(For mouse) We identified 4 such misassemblies in the HiCanu assembly, 6 in hifiasm and more than 100 in both Falcon and Peregrine.
(For the repeat-rich maize genome) There were 3 collapsed misassemblies in the hifiasm assembly and 9 in HiCanu, versus more than 100 in Falcon and Peregrine.
这个结果统计的表里,上面两个物种是近亲繁殖的后代,下面三个样本是杂交后代。上面这个misassemblies的数据怎么来的呢,就是将HiFi-read再用minimap2回贴到assembly上,然后调用一个检查SNPs(单核苷酸多态性的软件),说白了就是我们想检查HiFi-read和我们组装的assembly有没有(非测序错误)的差异。然后得到的这些SNPs我们只保留有75%平均测序深度支持的,然后又进行了一个cluster,两个SNPs距离小于10kb的就具为一类,并且保证聚为一类的SNPs的密度在1kb至少一个。如果cluster长度大于5kb且包含10个以上SNPs的我们确认为一个misassemblies。(我也不是很懂为什么要这么复杂2333) Hifiasm的速度也非常快,只用了三天就组装了27GB的加州红杉,Peregrine大概花了15天。
Fig.15 Statistics of nonhuman assemblies5.
Primary assembly of human genomes
下面是一些人类的数据集,QV指的是contig的碱基错误率,衡量方法大致是根据对同一样本的short reads中的31-mers和contigs的31-mers进行比较;Multicopy genes retained指的是,一些重复基因的保留情况,大致原理是利用已知的参考基因组和数据库的已知人类基因,鉴定一批multicopy genes,然后再比对到assembly上,计算
\[\lvert {MCinASM} \cap {MCinREF} \rvert/\lvert {MCinREF} \rvert\]就是这里的评价参数了。这里还有一个与之类似的评价指标,resolved bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs),这个BAC是我们构建人类染色体文库的时候常用的基因工程的载体,例如CHM13人类基因组数据就有了大概330个BAC组成,然后我们将BACs回贴到assembly上,如果一致性大于99.5%,这个BAC就视为resolved,这个标准有什么意义呢,如果BAC上带着一些比较复杂的染色体区域,而组装的contig从中间断掉了,那么这BAC就不能被resolved了。
Fig.16 Statistics of human primary assemblies5.
Haplotype-resolved assembly of heterozygous human genomes
FNR: the percentage of true variants that are missed in the assembly.
FDR: the percentage of assembly-based variant calls that are not called in the truth data.
FNR:本来应该出现的突变位点,但是没在assembly中出现。 FDR:assembly中认为的突变位点,但是真实数据里并没有。
下面的表格统计的是,如果有额外的测序数据,类似Hi-C或者trio data,那么hifiasm可以采用graph binning得到更长的contig(注:人类染色体总长约6Gb,单倍型3Gb,最长的染色体大概0.25Gb,最短的是38Mb左右,这里面contig的NG50是34Mb了,所以可以说基本是染色体规模的单倍型了)
Fig.17 Statistics of human primary assemblies5.
Reflection (about repeats)
这篇文章没有提及repeats的处理问题,但是如何解决repeats的问题在基因组的重构中是一个非常重要的问题。因为这篇文章没有具体介绍如何处理repeats的问题,所以在这一部分我做一点点自己的思考,看一看Hifiasm在运行的过程中repeats发生了什么,同时自己也借此梳理一下repeats在assembly graph中的结构,为自己未来的工作找找灵感。
首先介绍一下repeat的结构和形成过程(Repeats’ evolution),可以看到其实repeat是mosaic结构,也就是repeat区域中嵌套了sub-repeat,或者说基因组的repeat其实是sub-repeat的一种排列组合。而之所以形成这种结构,很有可能是发生了染色体的结构变异,然后多次结构变异的叠加,形成了这样sub-repeat的结构。
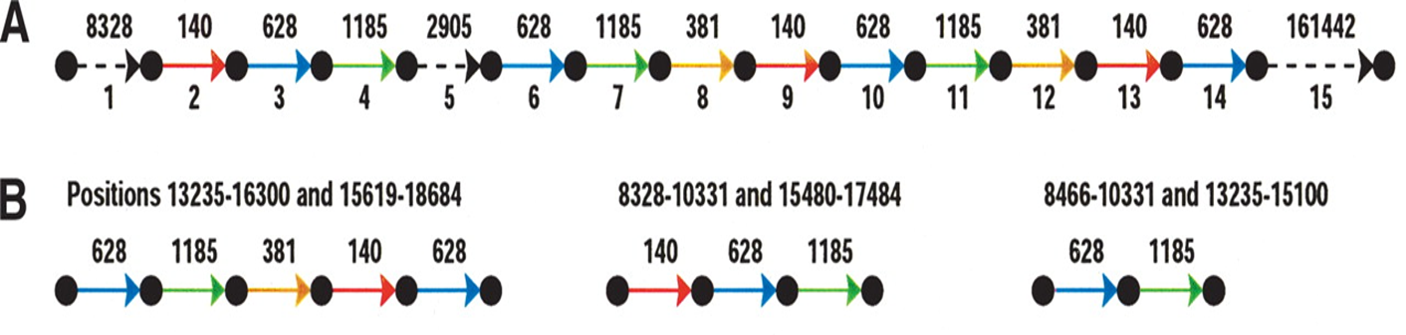 Fig.18 Repeat structure7.
Fig.18 Repeat structure7.
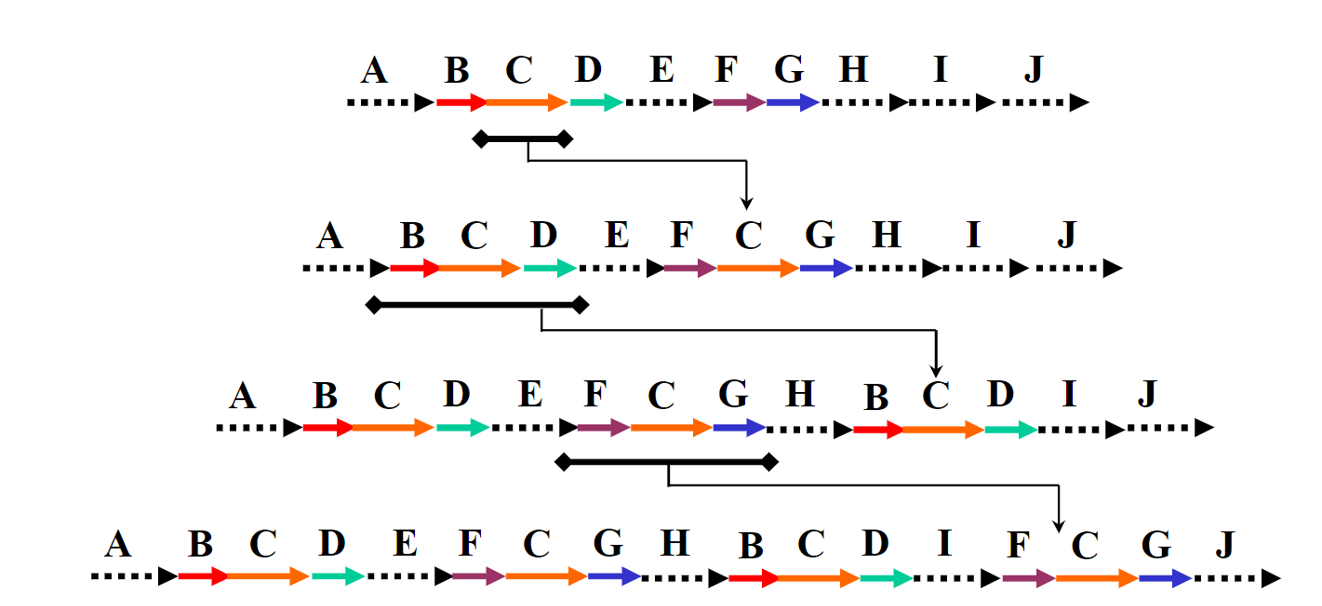 Fig.19 Repeat evolution8.
Fig.19 Repeat evolution8.
- 由于Hifi-read的长度前面提到平均可达13.5kb,虽然repeat的区域也许很长,但是sub-repeat的长度大部分没有那么长,所以因此很多repeat区域被read覆盖住了,那么构图的话也就不存在类似下面的情况
 Fig.20 Repeat in graph.
Fig.20 Repeat in graph.
- 如果sub-repeat的长度特别长,超过了13.5kb,下面为示意图,那么我们分成下面两种情况讨论
 Fig.21 An example of graph.
Fig.21 An example of graph.
⑴因为上面图中有三块repeat,所以非常有可能在在错误矫正的步骤中,read之间的overlap被判定为了inconsistent(如果在出现差异的位点,三块repeat贡献两个不同的碱基,那么就形成information positon,进而read的overlap被视为inconsistent)。因为hifiasm构图的时候只考虑consistent overlap,那么这些repeat产生的read在延伸的时候会各走各的路,在图中不会被合并为一条path,那么也就不会出现Fig.20的情况。
⑵如果非常不幸,repeat(及其附近)产生的read之间的连接被视为consistent(这可能需要出现差异的位点,三块repeat的碱基都不一致,所以不形成information position,而被进行错误矫正),那么会出现下面的图中的情况。如果形成wheal的情况,也就是紫色箭头所绘,文章并没有提及这种情况的处理方式,但是根据我之前阅读的文献,这种情况一般会被剪断,而形成tips;或者本来因为紫色区域的read中间覆盖确实,在string graph中本就是tips。 那么根据tips的修剪流程,这两个紫色的tips,因为和上面橙色,绿色箭头都没有同源性,所以会被断开,然后都放入primary assembly中,这样看来,虽然顺序有问题,但是最起码primary contig里面包含的序列还是比较全的。
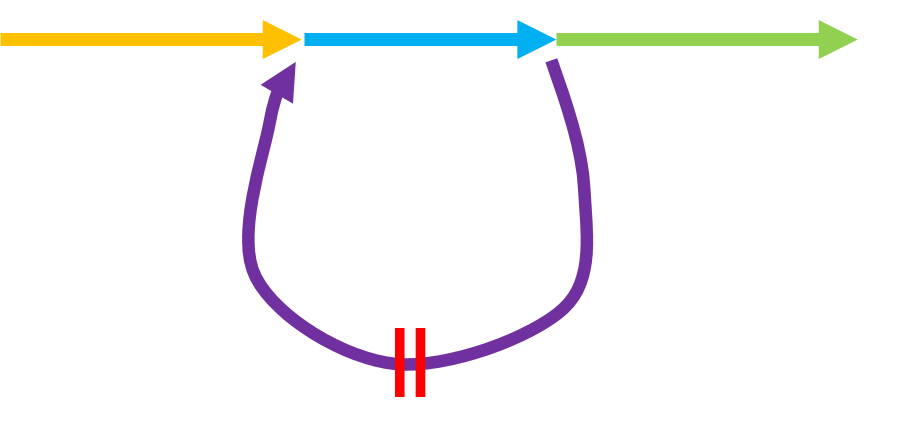 Fig.22 graph with consistent read overlap.
Fig.22 graph with consistent read overlap.
但是其实,repeat的结构如上介绍更复杂,同时,可以发现Fig.21中父源的染色体,我并没有再后面画上repeat,是因为我觉得既然是染色体结构变异,两个染色体的同一区域,位移到另一个区域,概率有些太小了。所以,非常有可能,紫色片段连接了绿色片段,那么string graph就会出现bubble和wheal同时存在的一个复杂结构。以上就是我的关于repeat问题的不完善的思考。
Reference
-
图片来源De novo assembly of haplotype-resolved genomes with trio binning ↩
-
图片来源Phased diploid genome assembly with single-molecule real-time sequencing ↩
-
图片来源Single-cell template strand sequencing by Strand-seq enables the characterization of individual homologs ↩
-
图片来源Haplotype-resolved de novo assembly using phased assembly graphs with hifiasm ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4 ↩5 ↩6
-
图片来源Haplotype-resolved de novo assembly using phased assembly graphs with hifiasm-Supplementary information ↩ ↩2
-
图片来源De novo repeat classification and fragment assembly: from de Bruijn to A-Bruijn graphs ↩